Dec 01, 2016 They have different uses. GUID partition table (GOT) is the scheme used by servers, Macs, and many contemporary Windows PCs. MacOS on Intel will only boot from a drive with a GUID partition table, and Windows systems from 2005 on can read/write th. As mentioned by the other comments, Apple's default partition scheme is to have everything on ONE partition. While not recommended (potentially due to not being easy to do), it is possible to move a home folder to a different partition. Here is how: Create a partition to use for the home folder (Disk Utility is the built-in choice to do so).
Choose OS X Extended (Journaled) for the Format, and, for the Scheme, choose GUID Partition Map. You could also choose MS-DOS as the format, if you want to be able to use the drive on both a Mac and a PC; this is helpful for flash drives, or portable USB drives. In that case, choose Master Boot Record for the Scheme. Honestly, the best partition scheme on any Mac is to avoid using partitions unless you need to run multiple operating systems or you need partitions that are formatted differently. The vast majority of Mac users gain no benefit by partitioning their Mac's hard drive.
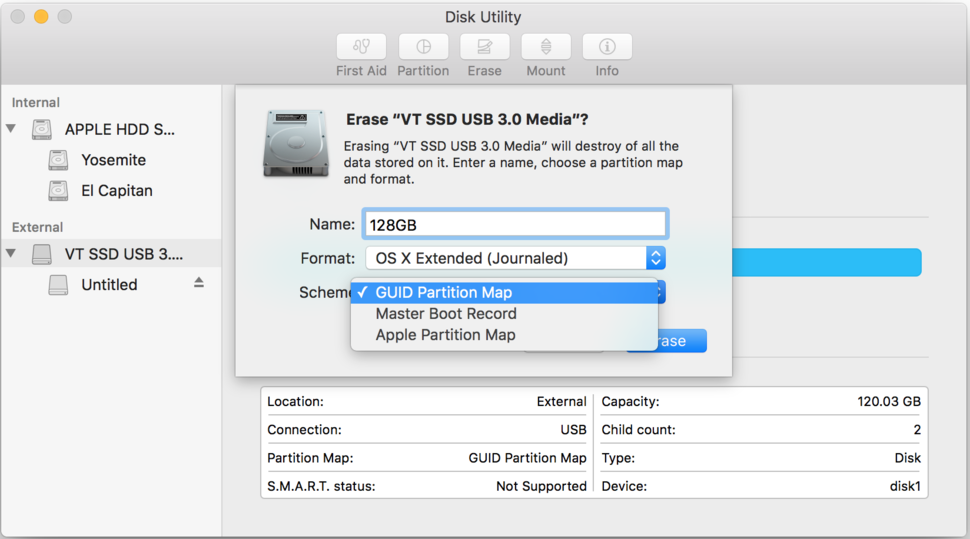
When you attach a storage disk to a Mac with the purpose of erasing or repartitioning it, you'll be presented with the option of selecting one of the three available partition maps: GUID Partition Map, Master Boot Record, and Apple Partition Map. In this article we will explain what a partition scheme is and which one to pick when formatting a drive.
What Is a Partition?
The fixed-sized subset of a disk drive treated as an individual unit by the operating system (in our case macOS) is defined as a partition. On every drive there are multiple partitions, and for this you will need a partition table or partition map – maintained by the operating system – to detail the status of the partitions.
Rbl posse ruthless by law zip reader. Download CleanMyMac X from MacPaw’s website and clean up to 500MB of junk data from your computer while enjoying all the features of the software without major limitations.
GUID Partition Map
This is a standard for the layout of the partition table on a storage disk using globally unique identifiers (GUIDs). As part of the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) standard, GUID is a bootable standard for systems with EFI firmware such as macOS. Non-Intel Macs won't support this bootable standard, hence the only option available to them is the Apple Partition Map (APM).
Apple Partition Map
Used on disks formatted for use with 68k and PowerPC Macs, the Apple Partition Map is the scheme that defines how the data is organized. Starting with OS X Tiger, both APM and GUID partitions can be used for accessing volumes, but PowerPC-based Macs can only boot from APM disks. While Intel-based Macs generally boot from a GUID Partition Table, they are all able to start the operating system from APM and Master Boot Record (MBR) using the BIOS-Emulation called EFI-CSM.
Master Boot Record
Introduced by IBM in 1983 to support the 10MB hard disk, the Master Boot Record is a type of boot sector developed for use with IBM PC systems. It is currently used for Windows partitions formatted as MS-DOS (FAT) or ExFAT.
Choosing a Partition Map
Now you know which partitioning map is which, the next time you insert an external drive or want to partition the built-in storage disk of the Mac, it will be easier to choose between the available options.
When formatting or erasing a volume with Disk Utility, you'll see a format menu prompt asking you to choose from:
- Mac OS Extended (Journaled)
- Mac OS Extended (Journaled, Encrypted)
- Mac OS Extended (Case-sensitive, Journaled)
- Mac OS Extended (Case-sensitive, Journaled, Encrypted)
- MS-DOS (FAT)
- ExFAT
- APFS (macOS High Sierra’s new file system)
- APFS (Encrypted)
- APFS (Case-sensitive)
- APFS (Case-sensitive, Encrypted).
Be aware that APFS is compatible only with macOS High Sierra and higher, so earlier versions of OS X or macOS won't mount an APFS volume. If you want maximum reach, Mac OS Extended (Journaled) is the right choice.
Below the file system format, the Disk Utility dialog box will list another contextual menu, the partition map scheme, which gives you another great tool to create targeted volumes. If you are looking to format a disk that will be shared with Windows users, the MBR scheme and MS-DOS (FAT) are the best choices. For drives used with Intel-based Macs only, the GUID Partition Map should the option to go for.
If you don't see the partition map scheme option, it is likely because Disk Utility doesn't list all volumes. This will prohibit Disk Utility from erasing the disk and show you an error message. To address this issue, you should click on the View button located in the top-left side of the Disk Utility dialog box and select “Show All Volumes”. From that point on, Disk Utility will ask for your partition map preference, and the formatting process will be smoother.
Best Mac Optimization Software of 2020
| Rank | Company | Info | Visit |
| |||
| |||
|
Get the Best Deals on Mac Optimization Software
Stay up to date on the latest tech news and discounts on Mac optimization software with our monthly newsletter.
Windows 10 Partition Scheme
- A swap partition (at least 256 MB) — swap partitions are used to support virtual memory. In other words, data is written to a swap partition when there is not enough RAM to store the data your system is processing.In years past, the recommended amount of swap space increased linearly with the amount of RAM in the system. But because the amount of memory in modern systems has increased into the hundreds of gigabytes, it is now recognized that the amount of swap space that a system needs is a function of the memory workload running on that system. However, given that swap space is usually designated at install time, and that it can be difficult to determine beforehand the memory workload of a system, we recommend determining system swap using the following table.
Amount of RAM in the System Recommended Amount of Swap Space 4GB of RAM or less a minimum of 2GB of swap space 4GB to 16GB of RAM a minimum of 4GB of swap space 16GB to 64GB of RAM a minimum of 8GB of swap space 64GB to 256GB of RAM a minimum of 16GB of swap space 256GB to 512GB of RAM a minimum of 32GB of swap space Table 7.3. Recommended System Swap Space
Note that you can obtain better performance by distributing swap space over multiple storage devices, particularly on systems with fast drives, controllers, and interfaces. A
The partition mounted on/boot/partition (250 MB)/boot/contains the operating system kernel (which allows your system to boot Fedora), along with files used during the bootstrap process. For most users, a 250 MB boot partition is sufficient.Btrfs
The GRUB bootloader does not support the Btrfs file system. You cannot use a btrfs partition for/boot.Note
If your hard drive is more than 1024 cylinders (and your system was manufactured more than two years ago), you may need to create a/boot/partition if you want the/(root) partition to use all of the remaining space on your hard drive.Note
If you have a RAID card, be aware that some BIOSes do not support booting from the RAID card. In cases such as these, the/boot/partition must be created on a partition outside of the RAID array, such as on a separate hard drive.A
This is where 'rootpartition (3.0 GB - 5.0 GB)/' (the root directory) is located. In this setup, all files (except those stored in/boot) are on the root partition.A 3.0 GB partition allows you to install a minimal installation, while a 5.0 GB root partition lets you perform a full installation, choosing all package groups.Root and
/rootThe/(or root) partition is the top of the directory structure. The/rootdirectory (sometimes pronounced 'slash-root') directory is the home directory of the user account for system administration.